产品信息
表达区间及表达系统(Source)
HSV-2 (HG52) Glycoprotein E, His Tag (GLE-H52H4) is expressed from human 293 cells (HEK293). It contains AA Ala 21 - Arg 414 (Accession # P89475).
Predicted N-terminus: Ala 21
Request for sequence
蛋白结构(Molecular Characterization)

This protein carries a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus.
The protein has a calculated MW of 45.0 kDa. The protein migrates as 50-60 kDa under reducing (R) condition (SDS-PAGE) due to glycosylation.
内毒素(Endotoxin)
Less than 1.0 EU per μg by the LAL method.
纯度(Purity)
>95% as determined by SDS-PAGE.
>90% as determined by SEC-MALS.
制剂(Formulation)
Lyophilized from 0.22 μm filtered solution in PBS, pH7.4 with trehalose as protectant.
Contact us for customized product form or formulation.
重构方法(Reconstitution)
Please see Certificate of Analysis for specific instructions.
For best performance, we strongly recommend you to follow the reconstitution protocol provided in the CoA.
存储(Storage)
For long term storage, the product should be stored at lyophilized state at -20°C or lower.
Please avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles.
This product is stable after storage at:
- -20°C to -70°C for 12 months in lyophilized state;
- -70°C for 3 months under sterile conditions after reconstitution.
产品数据图
电泳(SDS-PAGE)

HSV-2 (HG52) Glycoprotein E, His Tag on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 95%.
SEC-MALS
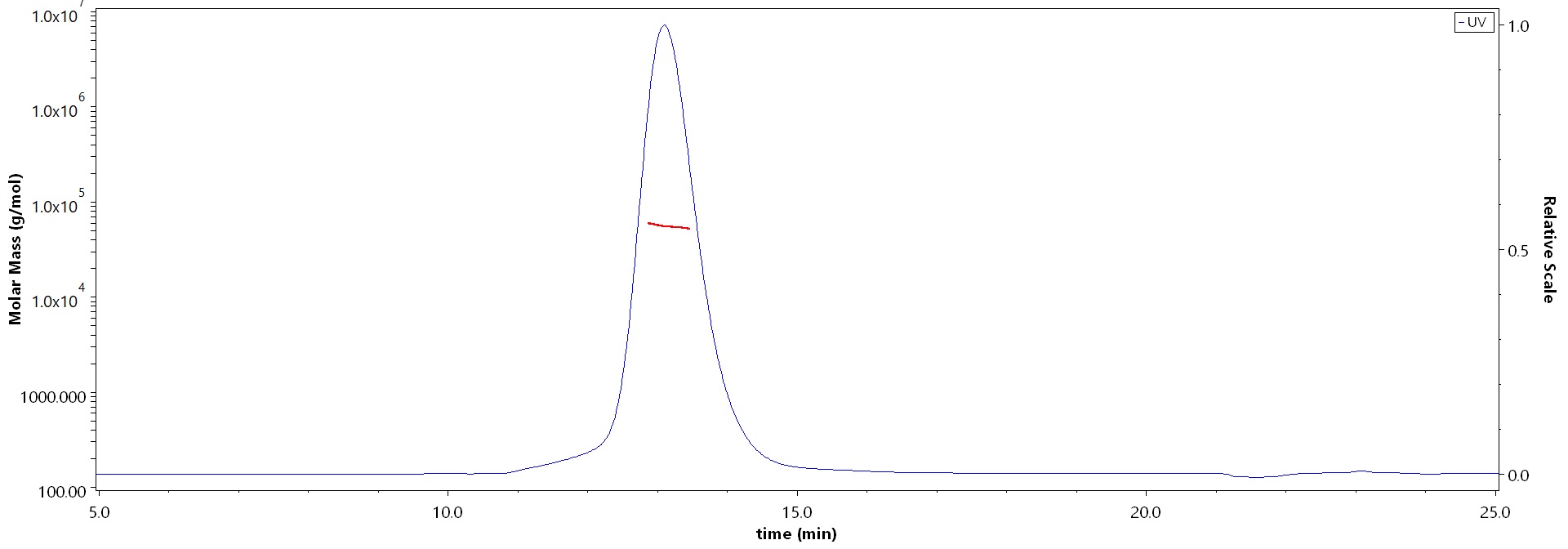
The purity of HSV-2 (HG52) Glycoprotein E, His Tag (Cat. No. GLE-H52H4) is more than 90% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 50-65 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
Report
活性(Bioactivity)-ELISA
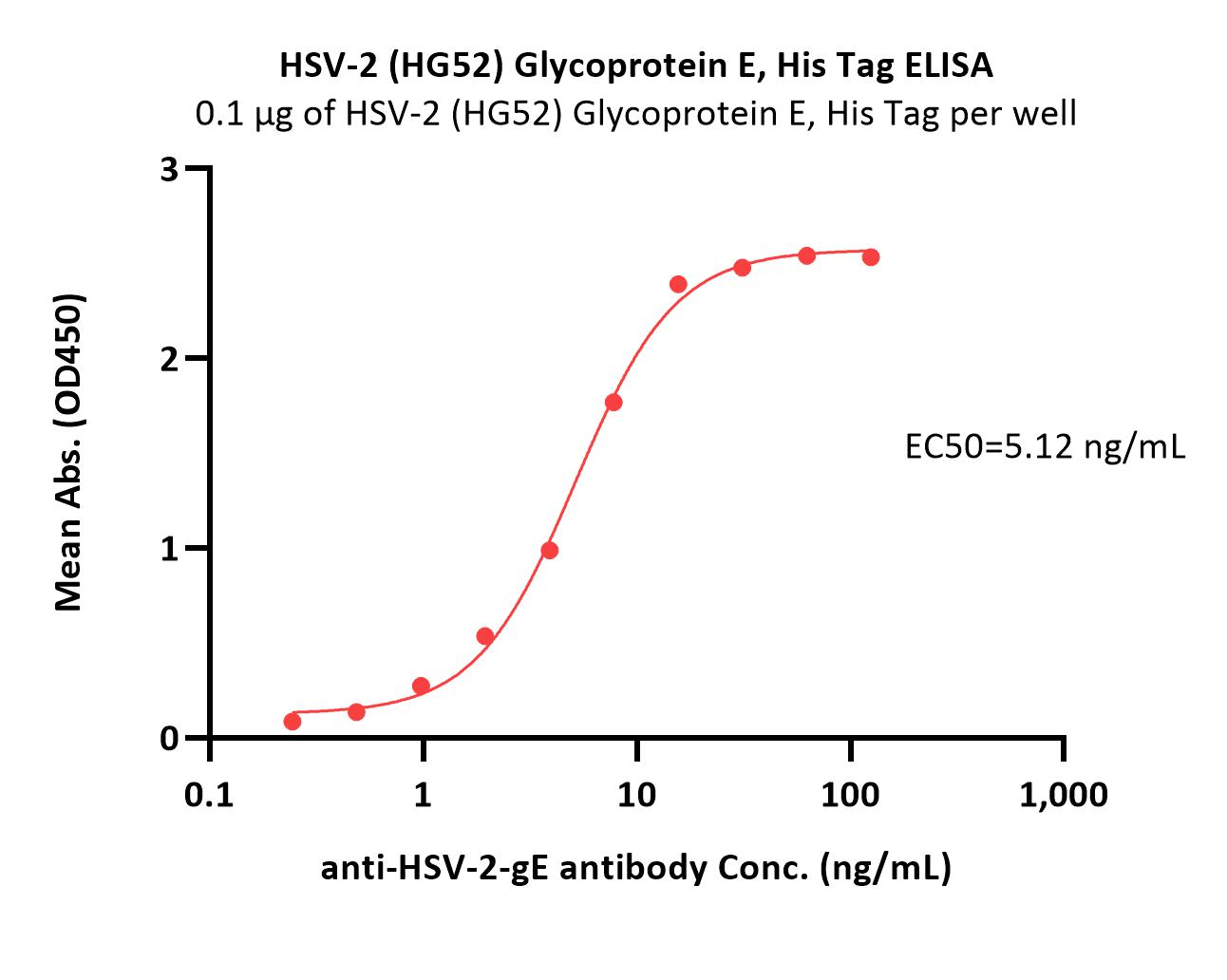
Immobilized HSV-2 (HG52) Glycoprotein E, His Tag (Cat. No. GLE-H52H4) at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind anti-HSV-2-gE antibody with a linear range of 0.2-16 ng/mL (QC tested).
Protocol
产品评论 发表评论

背景
Herpesvirus infections are widely spread throughout the world population. Herpes simplex virus (HSV) belongs to the α-herpesvirus subfamily. There are two main types of HSV, HSV-1 and HSV-2, which infect humans. HSV-2 mainly causes genital lesions, whereas HSV-1 is involved in both oral and genital infections. In epithelial cells, the heterodimer gE/gI is required for the cell-to-cell spread of the virus, by sorting nascent virions to cell junctions. Once the virus reaches the cell junctions, virus particles can spread to adjacent cells extremely rapidly through interactions with cellular receptors that accumulate at these junctions. Implicated in basolateral spread in polarized cells. In neuronal cells, gE/gI is essential for the anterograde spread of the infection throughout the host nervous system.














