产品信息
- Genetically modified cell lines best reflect MOA (Mechanism of Action)
- Higher activity and larger assay window for robust and reproducible cell-based bioassay
- Comprehensive application data to support assay development and validation
- Full tracible record, stringent quality control and validated cell passage stability
- Parental cell line legally obtained from internationally recognized cell resource bank and commercially licensed
- Global commercial license assistance whenever regulatory filing is required
描述(Description)
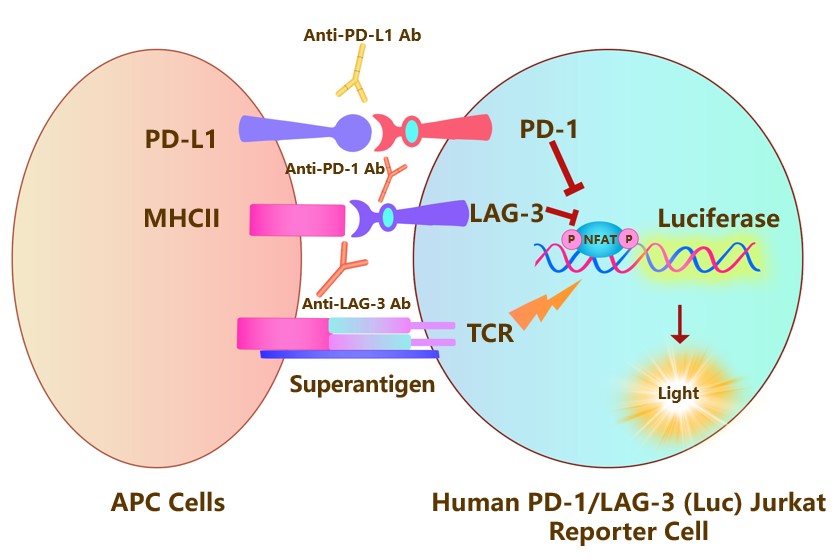
The Human PD-1/LAG-3 (Luc) Jurkat Reporter Cell was engineered to not only express the NFAT response element driving luciferase expressing systems, but also express the receptors full length human PD-1 (Gene ID: 5133) and LAG-3 (Gene ID: 3902), which can use to evaluate the synergistic effect of anti-human PD-1 and anti-human LAG-3 antibody. When co-cultured with target cells expressing human PD-L1 and MHCⅡ, the PD-1/PD-L1 and LAG-3/MHCⅡ interactions inhibit TCR signaling and NFAT-mediated luminescence. Blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 and LAG-3/MHCⅡ interactions by the stimultaneous addition of anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 and anti-LAG-3 antibodies release the inhibitory signals and result in TCR activation and NFAT-mediated luminescence.
应用说明(Application)
• Screen for anti-human PD-1 or/and anti-human LAG-3 antibody
生长特性(Growth Properties)
Suspension
筛选标记(Selection Marker)
Puromycin (5 μg/mL) + Hygromycin (20 μg/mL)
培养基(Complete Growth Medium)
RPMI-1640 + 10% FBS
冻存液(Freeze Medium)
Serum-free cell cryopreservation medium
装量(Quantity)
1 vial contains at least 5×10^6 cells in 1 mL serum-free cryopreservation medium
存储(Storage)
Frozen in liquid nitrogen.
支原体检测(Mycoplasma Testing)
Negative
无菌检测(Sterility Testing)
Negative
使用说明(Instructions for Use)
See data sheet for detailed culturing and assay protocol.
产品数据图
Receptor Assay
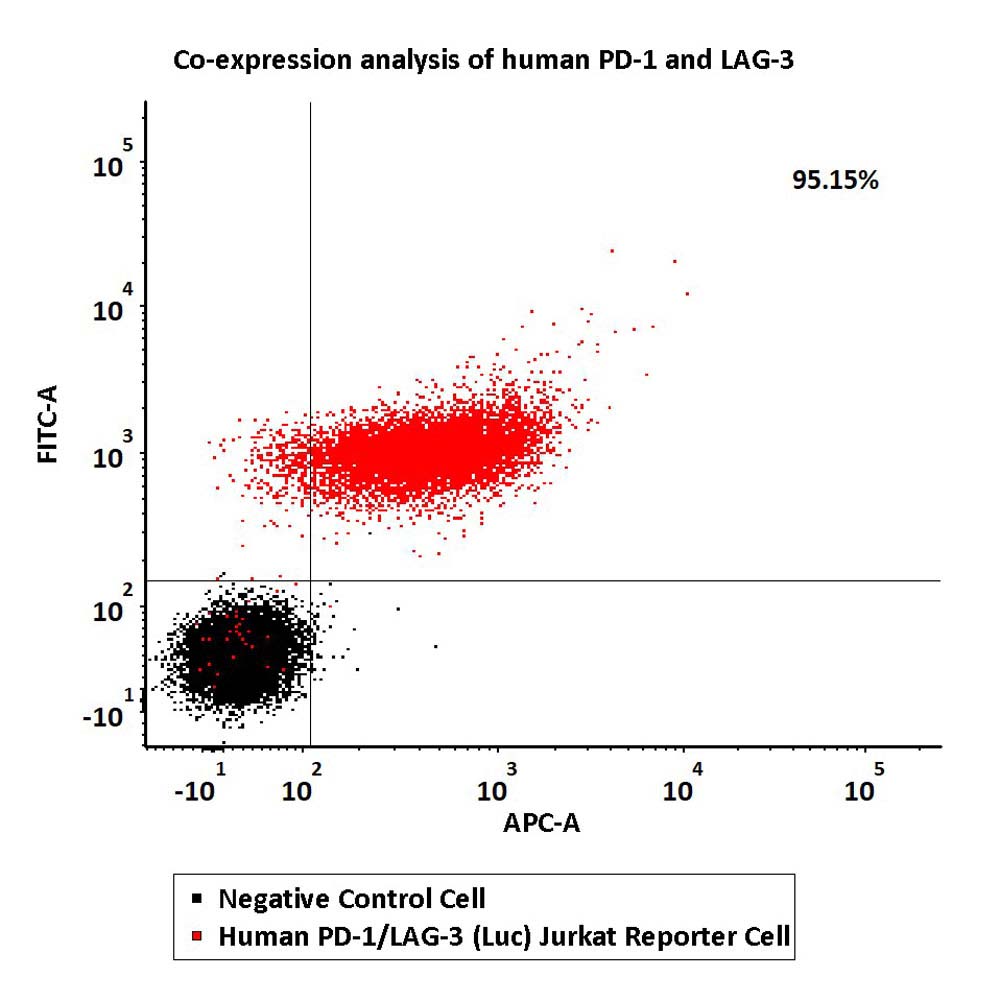
Co-expression analysis of human PD-1 and LAG-3 on Human PD-1/LAG-3 (Luc) Jurkat Reporter Cell by FACS.
Cell surface staining was performed on Human PD-1/LAG-3 (Luc) Jurkat Reporter Cell or negative control cell using FITC-labeled anti-human PD-1 antibody and APC-labeled anti-human LAG-3 antibody.
Protocol
Application
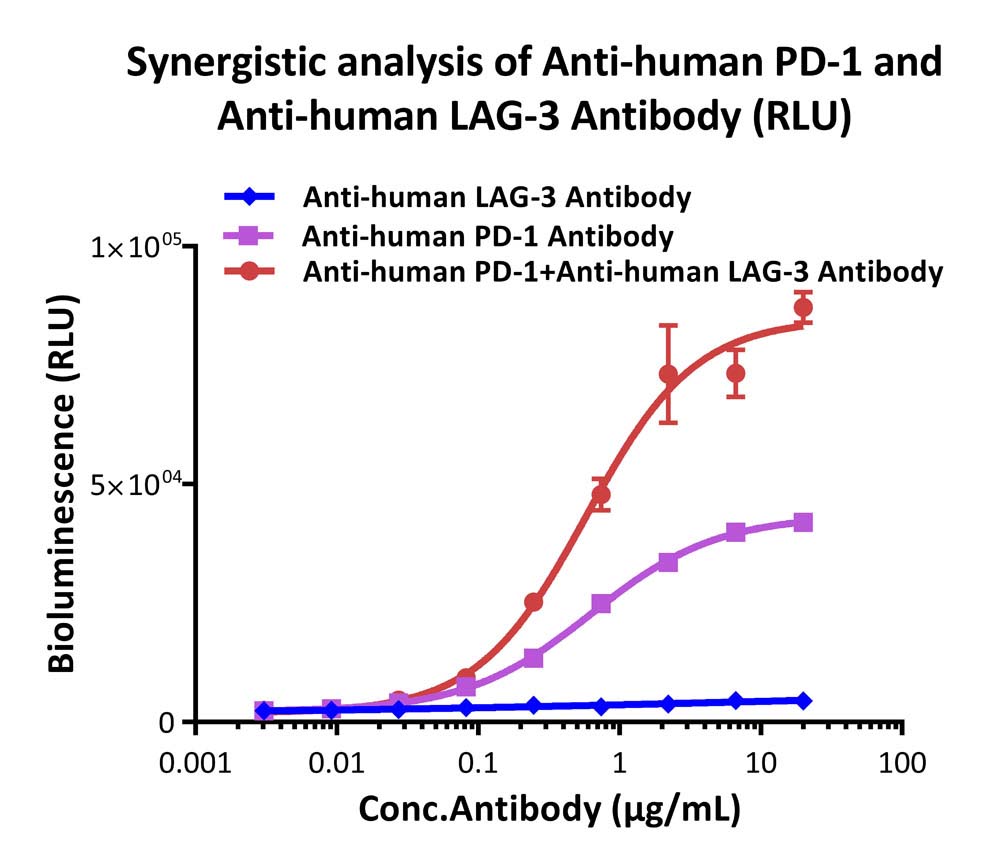
Analysis of the synergistic effect for anti-human PD-1 and anti-human LAG-3 antibody (RLU).
This reporter cell was co-incubated with serial dilutions of anti-human PD-1 plus anti-human LAG-3 antibody in the presence of target cells expressing human PD-L1 and MHCⅡ. The EC50 was approximately 0.58 μg/mL.
Protocol
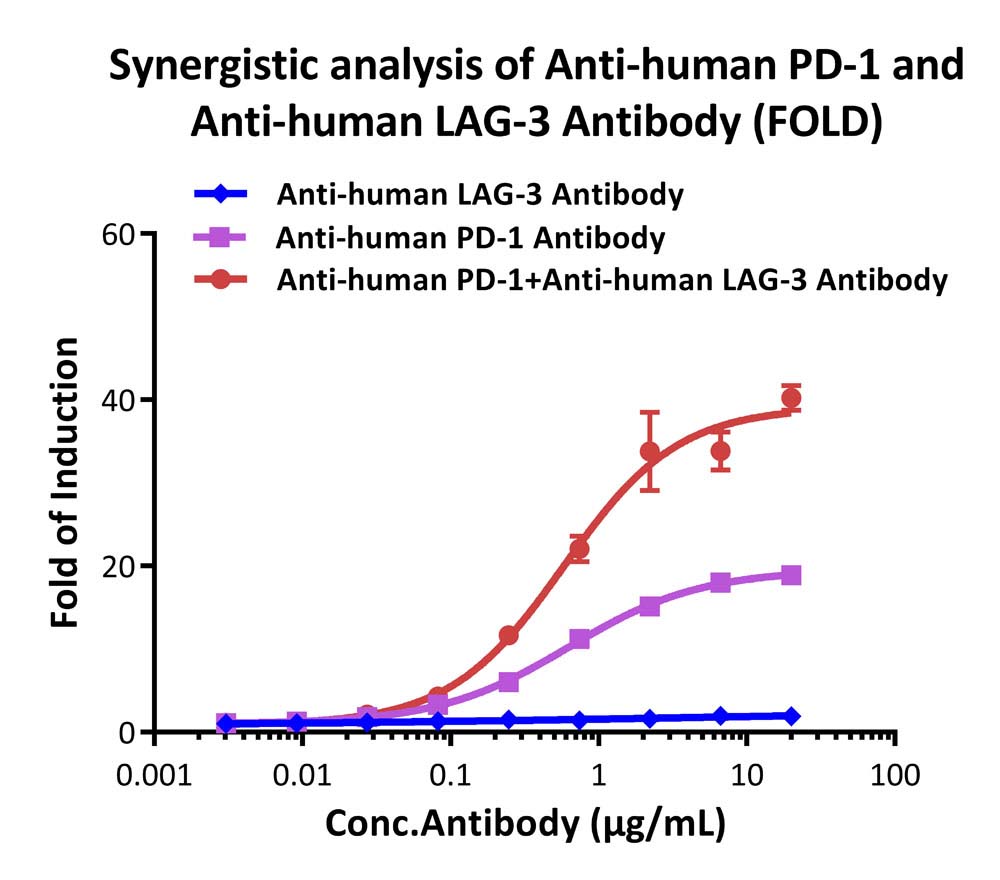
Analysis of the synergistic effect for anti-human PD-1 and anti-human LAG-3 antibody (FOLD).
This reporter cell was co-incubated with serial dilutions of anti-human PD-1 plus anti-human LAG-3 antibody in the presence of target cells expressing human PD-L1 and MHCⅡ. The max induction fold was approximately 40.
Protocol
Passage Stability
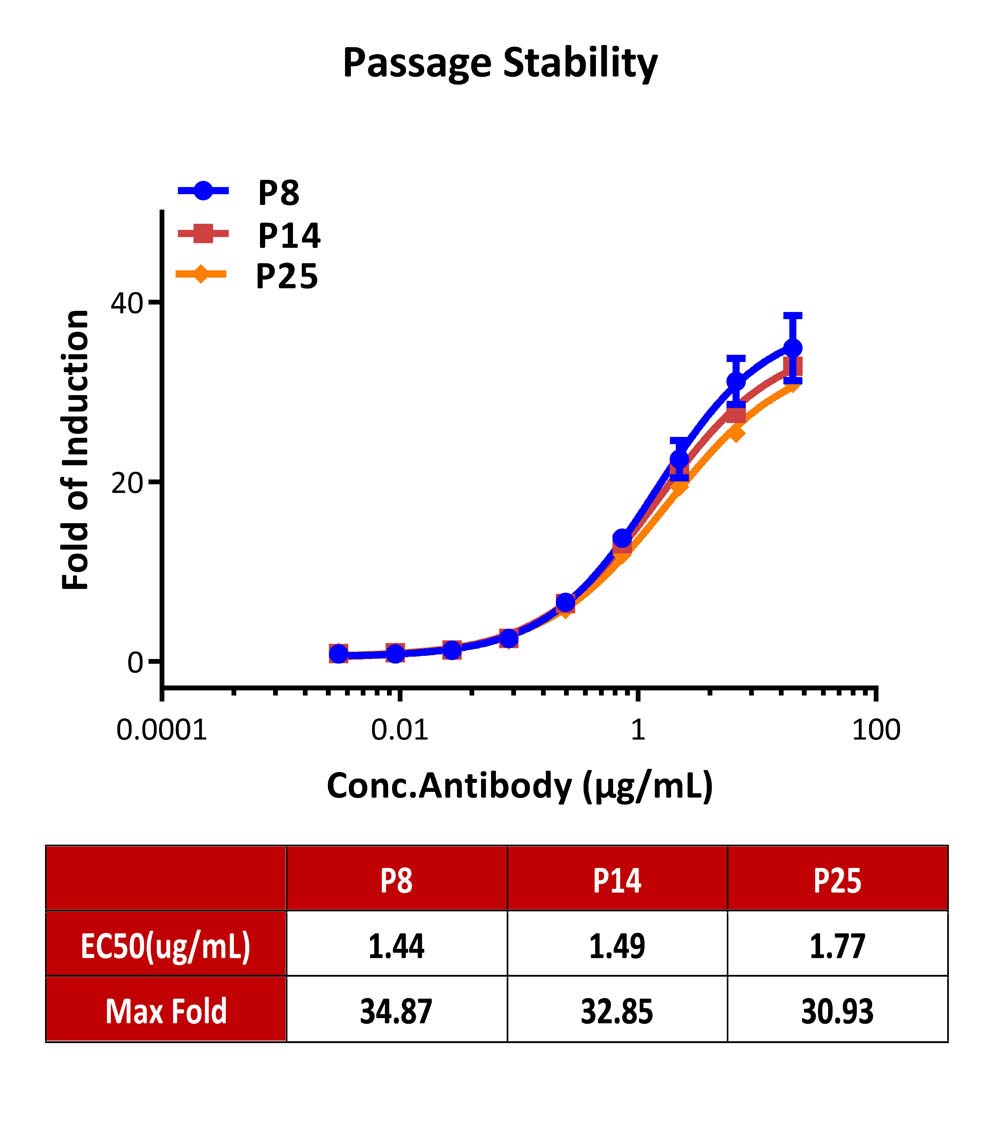
Passage stability analysis by Signaling Bioassay.
The continuously growing Human PD-1/LAG-3 Jurkat Reporter Cell was stimulated with serial dilutions of anti-human PD-1 plus anti-human LAG-3 antibody in the presence of target cells expressing PD-L1 and MHCⅡ. Anti-human PD-1 plus anti-human LAG-3 antibody stimulated response demonstrates passage stabilization (fold induction and EC50) across passage 8-25.
Protocol
产品评论 发表评论

背景
Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) is also known as CD279 and PDCD1, is a type I membrane protein and is a member of the extended CD28/CTLA-4 family of T cell regulators. PDCD1 is expressed on the surface of activated T cells, B cells, macrophages, myeloid cells and a subset of thymocytes. PD1 inhibits the T-cell proliferation and production of related cytokines including IL-1, IL-4, IL-10 and IFN-γ by suppressing the activation and transduction of PI3K/AKT pathway.
Lymphocyte activation gene 3 protein (LAG3) is also known as CD antigen CD223 and protein FDC, which belongs to immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. As a CD4 homologue, LAG3 expressed on the surface of activated conventional T cells and regulatory T (Treg) cells. In conventional T cells, LAG-3 acts as an inhibitory receptor of T cell inflammation.














